|
|
|

|



|
|
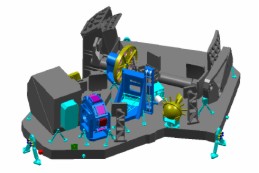
General presentation of the JWST/NIRSpec project: The future space telescope JWST (James Webb Space telescope), developed jointly by the American, European and Canadian space agencies (NASA, ESA and CSA), is scheduled for launch in 2018. Advertised as the successor of the Hubble space telescope (HST), it is a passively-cooled 6.5m telescope that will observe from 0.6 to 25 µm As part of its overall contribution to the JWST project, the European Space Agency provides the near-infrared spectrograph NIRSpec, that has been built by EADS-Astrium (nowadays AIRBUS Defence & Space). NIRSpec is a multi-object spectrograph that will allow astronomers to obtain the spectra of more than one hundred objects per field of view in one shot. One of its major scientific goals will be the study of the formation and evolution of the first stars and galaxies. It will cover the wavelength range extending from 0.6 µm to 5.0 µm. The target selection will be performed using a fully-addressable array of micro-shutters developed by the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in the USA. In addition to the MOS mode, NIRSpec has an integral field spectrograph mode (IFS mode, continuous coverage of a small field of view with high spatial and spectral resolutions) and a classical long-slit spectrograph mode. |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The contribution of CRAL to the NIRSpec project: The CRAL is involved in the JWST/NIRSpec project since its early phases and has been the only european institute directly involved in the project through a contract with EADS-Astrium. We were responsible for:  the instrument performance simulator software, the instrument performance simulator software, the instrument performance and calibration aspects within the core NIRSpec engineering team of EADS Astrium, the instrument performance and calibration aspects within the core NIRSpec engineering team of EADS Astrium, the link between the industrial company and the ESA instrument science team, the link between the industrial company and the ESA instrument science team, support to the industrial development team for the development of the target acquisition procedures and of the quick look analysis and calibration software. support to the industrial development team for the development of the target acquisition procedures and of the quick look analysis and calibration software.This contract was over end July 2011 after the final software delivery and the team participation to the tests conducted on the instrument at EADS premises. A new contract was signed in 2017 with ESA to update the software with a reduced development team. This contract ended in 2021. Related links:  French version of this page / Version française de cette page French version of this page / Version française de cette page  JWST at NASA JWST at NASA  The Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon (CRAL) The Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon (CRAL) |
The development team at CRAL :
The development team of the former contract at CRAL :
Where members of the team:
The associated scientists at CRAL:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||
| Created by: | Pierre Ferruit | 21.12.2004 | Back to CRAL home page | |
| Last change: | Arlette Pecontal | 14.09.2022 | ||